Difference between SDS, SDS Plus.
The SDS model drill comes in a variation of drill bits which are typically easy to understand; Hilti and bosch developed the SDS drill bit in 1975, designed in Germany. The name SDS translates in german as Stecken – Drehen – Sichern, meaning Insert, twist secure.
The original SDS design by Bosch in the 1970s had a quick release concept that enables the user to insert the drill into a snap-in clutch.
The idea was to provide a more efficient system of delivering a hammer blow to the end of a drill bit while rotating without impacting the chuck. Because of the machined hollowed out section in the drill’s shank end, the bit can move freely but within limits when struck by the continuous hammer mechanism in the drill body.
Two slots are machined opposite one another to lock the bit into position. This whole concept makes a far more comfortable working environment for the user and minor wear and tear in the chuck.
The diameter of an SDS and SDS Plus shank is 10 millimetres. (The SDS Max is 18 millimetres. The SDS Quick is 6 mm.)
What is the difference?
The SDS shank has the advantage of fitting into a simple spring-loaded chuck so that you can push into the chuck without tightening. The shank and the chucks made for it are especially suited to hammer drilling with masonry drills in stone and concrete.
The drill bit is not held solidly in the chuck but can slide back and forth like a piston, it does not slip during rotation due to the non-circular shank cross-section, matching the chuck. The drill bit’s hammer acts to accelerate only the drill bit itself and not the large mass of the chuck, which makes hammer drilling with an SDS shank drill bit much more productive than with other types of the shank.
The rotational drive uses the sliding keyways that open to the end of the shank, which mate with keys in the chuck. The chuck grasps the more minor indentations that do not open to the end to prevent the drill bit from falling out. The hammer of the drill hits the flat end of the shank. Lubricate the shank with grease to allow it to slide in the chuck.
Sizes
There are four standard sizes of SDS: SDS Quick, SDS-plus (or SDS-plus or SDS+), SDS-Top and SDS-max. SDS-plus is the most common by counting tools manufactured and sold, with masonry drills from 4 mm diameter to 30 mm (and from 5/32″ to 1-1/4″) diameter ordinarily available. The shortest SDS-plus masonry drill bits are about 110 mm overall length and the most extended 1500 mm.
SDS-max is more common for more giant rotary hammers and chipping guns, and standard sizes start at 1⁄2 inch (13 mm) diameter up to 1 3⁄4 inches (44 mm) diameter. Standard lengths are 12 to 21 inches (300 to 530 mm). Hilti’s TE-S system is similar to these SDS systems. Still, it is for chipping only and not rotation, in tools for applications more extensive than could be handled by SDS-Max (e.g. demolition of concrete walls or floors).
Types of SDS Connection
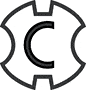
SDS Plus (TE-C)
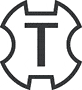
The SDS Top (TE-T)
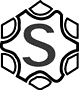
SDS Max (TE-Y)

Hilti TE-S
To choose the correct drill bit, you can check your drill user manual and determine what drill bit you will need.
The Best Masonry Drill Bits – Click Below
